

Spinal rotation mobilizations can help improve range of motion in the thoracic spine by targeting the specific joints and soft tissues involved in rotation. By applying controlled and gentle rotational forces, these mobilizations can help stretch tight muscles, release adhesions, and improve joint mobility in the thoracic region. This can lead to increased flexibility, reduced stiffness, and enhanced overall function of the thoracic spine, allowing for better movement and posture.
The key differences between passive and active spinal rotation mobilizations lie in who is initiating the movement. Passive mobilizations involve the therapist applying the rotational force to the patient's spine, while active mobilizations require the patient to actively participate in the movement by engaging their own muscles. Passive mobilizations are often used initially to assess and address restrictions, while active mobilizations can help improve neuromuscular control and functional movement patterns.
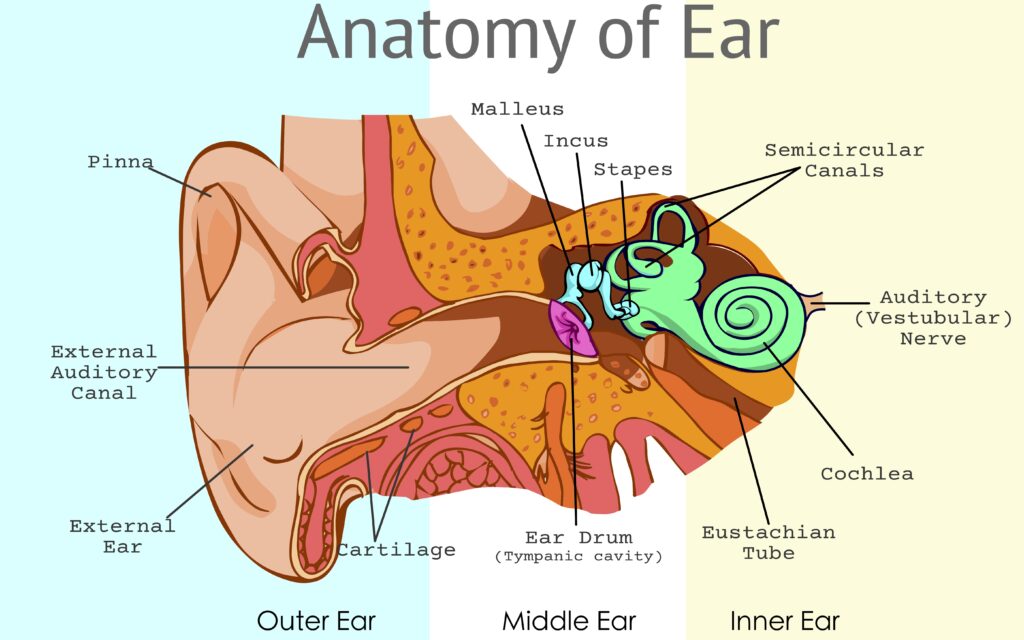
The Vestibular system’s role is to maintain clear vision with gazing, maintain stability to limbs during head movements, and maintain spatial orientation. You can develop dysfunction in the vestibular system from a variety of causes: toxins, diseases, autoimmune diseases, infection, injury, and even just plain aging. The post <strong>What is Vestibular?</strong> appeared first on React Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-03-22
There are three “basic” balance activities that we use not only to test balance, but to practice with too! Progressions: Ways The post 3 Exercises Used to Test and Strengthen Your Balance appeared first on React Physical Therapy.

Posted by on 2023-03-13
The simple task of bending over to pick something up can hurt your back if you perform the motion incorrectly. Learning a simple movement pattern called a hip hinge can prevent back pain. The post How To Do a Proper Hip Hinge Exercise appeared first on React Physical Therapy.

Posted by on 2023-03-08
Picture your day. If you commute to and from work by car you are most likely sitting. If you have an office job, you likely sit in front of a computer. If you are a student, you sit in the classroom. And it's not just during the day. When you get home you probably sit to eat dinner and then head to your comfy couch to, once again, SIT and watch your favorite television show. Before you know it, it's bedtime and this routine start all over again the next morning. The post Three Tips to Fight the Effects of Sitting appeared first on React Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-03-08
There are certain contraindications for using spinal rotation mobilizations in patients with specific spinal conditions, such as acute fractures, severe osteoporosis, spinal instability, or spinal cord compression. These conditions may be exacerbated by rotational forces applied to the spine, leading to further injury or complications. It is important to carefully assess each patient's medical history and condition before incorporating spinal rotation mobilizations into their treatment plan.

Spinal rotation mobilizations can be incorporated into a comprehensive treatment plan for patients with low back pain by addressing any restrictions or dysfunctions in the thoracic spine that may be contributing to the pain. By improving thoracic mobility and alignment, spinal rotation mobilizations can help reduce stress on the lumbar spine and surrounding structures, leading to decreased pain and improved function. These mobilizations can be combined with other interventions such as strengthening exercises, manual therapy, and education on proper body mechanics.
Common techniques used for performing spinal rotation mobilizations in a clinical setting include passive rotational stretches, joint mobilizations, muscle energy techniques, and spinal manipulation. These techniques are typically performed by trained healthcare professionals, such as physical therapists or chiropractors, who have expertise in assessing and treating spinal dysfunctions. The choice of technique may vary depending on the patient's condition, preferences, and response to treatment.

Spinal rotation mobilizations may help alleviate symptoms of sciatica or radiculopathy by addressing any restrictions or imbalances in the thoracic spine that could be contributing to nerve compression or irritation. By improving thoracic mobility and alignment, these mobilizations can help reduce pressure on the nerves and promote better nerve function. However, it is important to individualize the treatment approach based on the specific needs and responses of each patient with sciatica or radiculopathy.
When performing spinal rotation mobilizations on elderly patients or individuals with osteoporosis, specific precautions should be taken to ensure safety and prevent injury. It is important to use gentle and controlled rotational forces, avoid excessive twisting or torque on the spine, and monitor for any signs of discomfort or instability. Additionally, it may be necessary to modify the techniques or intensity of mobilizations based on the individual's bone density, joint health, and overall physical condition. Consulting with a healthcare provider or specialist experienced in working with these populations is recommended to ensure appropriate and effective treatment.
Therapeutic exercises play a crucial role in managing symptoms of frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) by improving range of motion, reducing pain, and enhancing overall function of the affected joint. These exercises typically focus on stretching and strengthening the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, such as the rotator cuff muscles and deltoids, to help loosen the tight capsule and improve flexibility. By incorporating exercises that target specific muscle groups, individuals with frozen shoulder can gradually regain mobility and alleviate stiffness. Additionally, therapeutic exercises can also promote blood flow to the affected area, which aids in reducing inflammation and promoting healing. Overall, a structured exercise program tailored to the individual's needs can significantly contribute to the management of frozen shoulder symptoms and facilitate a quicker recovery.
Therapeutic exercises, such as physical therapy, can play a crucial role in managing symptoms of degenerative disc disease. These exercises focus on improving flexibility, strength, and posture, which can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with the condition. By targeting specific muscle groups and promoting proper spinal alignment, therapeutic exercises can reduce pressure on the affected discs and improve overall function. Additionally, exercises that emphasize core stability and balance can provide support to the spine and prevent further degeneration. Incorporating a tailored exercise regimen into a comprehensive treatment plan can enhance mobility, reduce inflammation, and enhance the quality of life for individuals with degenerative disc disease.
There are several exercises that can help improve thoracic spine extension, such as thoracic extension mobilizations, foam rolling, cat-cow stretches, thoracic extensions over a foam roller, and thoracic spine rotations. These exercises target the muscles and joints in the thoracic spine region, promoting increased flexibility, mobility, and extension. By incorporating these specific exercises into a regular workout routine, individuals can work towards improving their thoracic spine extension and overall spinal health. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or fitness trainer before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure proper form and technique to prevent injury.
The best exercises for strengthening the muscles around the knee joint include leg presses, squats, lunges, step-ups, and hamstring curls. These exercises target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles, which are essential for providing stability and support to the knee joint. Additionally, incorporating exercises that focus on the hip abductors and adductors, such as clamshells and hip bridges, can help improve overall lower body strength and reduce the risk of knee injuries. It is important to perform these exercises with proper form and gradually increase the intensity to avoid putting excessive strain on the knee joint. Stretching exercises like quad stretches and hamstring stretches can also help improve flexibility and reduce tightness in the muscles surrounding the knee.
Therapeutic exercises, such as physical therapy and occupational therapy, have been shown to significantly improve mobility in individuals who have experienced a stroke. These exercises focus on improving strength, flexibility, balance, coordination, and overall motor function. By targeting specific muscle groups and movements affected by the stroke, individuals can regain control and function in their limbs and body. Additionally, exercises that incorporate repetitive movements and task-specific activities can help retrain the brain and nervous system to adapt and compensate for any deficits caused by the stroke. Overall, engaging in a structured and consistent therapeutic exercise program can lead to notable improvements in mobility and quality of life for stroke survivors.
The best exercises for improving hip internal rotation range of motion include clamshells, seated hip internal rotation stretches, hip internal rotation mobilizations, and hip internal rotation strengthening exercises such as hip internal rotation with resistance bands or cable machines. These exercises target the muscles responsible for hip internal rotation, such as the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae. By incorporating a combination of stretching, mobilization, and strengthening exercises, individuals can effectively increase their hip internal rotation range of motion and improve overall hip function. It is important to perform these exercises with proper form and gradually increase intensity to avoid injury and maximize results.
Therapeutic exercises for treating patellar tendonitis focus on reducing inflammation and pain in the patellar tendon, typically involving stretching and strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and hamstrings. These exercises may include eccentric exercises, isometric exercises, and proprioceptive training to improve stability and reduce stress on the tendon. In contrast, therapeutic exercises for treating patellar tendinopathy aim to address the underlying degenerative changes in the tendon, focusing on eccentric strengthening exercises, plyometric exercises, and progressive loading to promote tendon healing and remodeling. Additionally, exercises for patellar tendinopathy may involve addressing biomechanical factors such as muscle imbalances and faulty movement patterns to prevent further injury and promote optimal tendon function.